You’ve probably heard that Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning are the future. But what exactly do they mean? These innovations have transformed society and have had a big influence on modern technology.
These technologies are employed in the development of intelligent applications and devices.
In this article, we will look at Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) in all their brilliance and how they differ.
The Relationship Between Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, And Deep Learning
The idea of artificial intelligence is to create intelligent and smart machines.
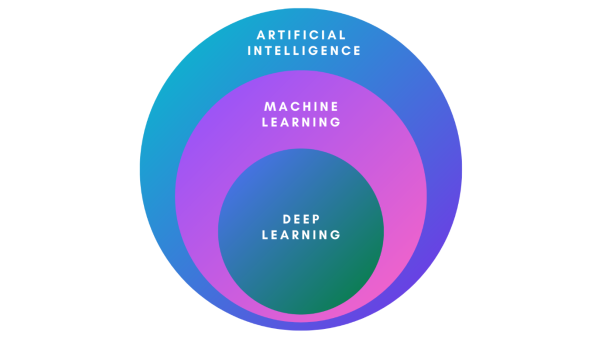
Machine Learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that allows you to build applications with AI.
Deep learning can be classified as a subset of machine learning, which consists of algorithms that use large amounts of data.
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning, which is a subset of artificial intelligence. This sounds complicated, but don’t worry—we’ve got you covered.
The term “artificial intelligence” (AI) refers to a broad spectrum of disciplines and technology. The creation of methods and models that enable a computer system to learn from data is the emphasis of the ML area of AI. Deep learning (DL) is a branch of machine learning that focuses on using deep neural networks for complex challenges.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
In its broadest sense, Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to a robot or digital computer’s capacity to carry out actions typically performed by intelligent beings.
The concept is widely used in reference to the task of creating artificial intelligence (AI) systems that possess human-like cognitive abilities, such as the capacity for reasoning, generalization, and experience-based learning.
The majority of Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems mimic natural intelligence to handle complex challenges. AI technology is used, for instance, by virtual personal assistants like Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, and Google Assistant to comprehend and carry out user orders.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
Several sub-types of Artificial Intelligence (AI) are classified according to their functionality, such as:
These are unable to predict future responses. Simply put, they have access to the information at hand and lack any memory.
Applications of AI
AI is practically used everywhere in the twenty-first century, from chatbots to virtual assistants. Among many other applications of Artificial Intelligence (AI), they include the following:
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence, so even though all machine learning involves (AI), not all (AI) involves machine learning.
Machine learning is a type of (AI) that enables software programs to improve their accuracy in predicting events without being explicitly programmed. The fundamental concept is to empower machines with more processing power and data storage to train themselves.
To uncover patterns in large data sets, machine learning algorithms employ statistical methods. The algorithms get more precise and can make better predictions as more data is gathered and examined.
For instance, companies like Netflix, Amazon, and Spotify use machine learning algorithms to suggest products, movies, or songs based on a user’s previous preferences.
The 3 Types of Machine Learning
According to its functionality, Machine Learning (ML) is further classified into three primary categories:
This indicates that the input and associated output values make up the dataset. The algorithm learns the underlying pattern using the input values and can then predict the output values for fresh input values.
Risk analysis, fraud detection, spam filtering, and other real-world applications use supervised learning.
The system can analyze considerably bigger datasets since it does not require human labor to make the dataset machine-readable.
Due to the machine’s ability to swiftly analyze a vast quantity of data and generate predictions without the need for manual labeling, unsupervised learning is significantly more effective than supervised learning.
The machine then adjusts its settings based on this input to improve how well it completes the task.
Applications of Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is used in a broad range of areas and industries, including but not limited to:
What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks, which are multi-layered algorithms structures that draw inspiration from how the human brain works. Deep learning techniques use several layers to extract more complex characteristics from the input data.
Deep learning is based on artificial neural networks. These algorithms can learn more complicated functions than conventional machine learning algorithms because they use multiple layers and bigger datasets. Image recognition is an example of deep learning.
Deep learning algorithms are trained on a sizable dataset of images to recognize objects, people, sceneries, and other elements inside a picture.
Types of Deep Learning
Deep learning is further categorized into the following categories:
After receiving an image as input, a different set of steps is applied to each layer of the CNN. Next, the previous layer’s output is passed on to the subsequent stage, and so on. When CNN reaches the final layer, it can identify and classify objects in the image.
Recurrent neural networks are perfect for speech recognition, natural language processing, and time-series forecasting.
Applications of Deep Learning
Deep learning (DL) has several uses in a variety of areas, such as:
Differences Between Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, And Deep Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a catch-all phrase for any computer system that can do activities that would normally need human intellect. Deep learning (DL) is a branch of AI that focuses on learning from data using large datasets and sophisticated algorithms. Another branch of AI, machine learning (ML), focuses on using algorithms to find patterns in data and apply that knowledge to make predictions.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Deep Learning (DL), and ML are three related but separate ideas, in the field of computer science.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Deep learning (DL), and Machine Learning (ML) are expected to significantly influence various industries in the future, including healthcare, finance, transportation, and more.
Technology will grow increasingly intertwined in our daily lives as it develops, opening new uses and enhancing those already present.
Who knows, maybe one day Artificial Intelligence (AI), Deep learning (DL), and Machine Learning (ML) will even take over as the household pet of choice!
Frequently Asked Questions
What jobs will be replaced by AI?
This includes data entry and coding, support roles such as answering frequently asked questions, completing translation tasks, as well as writing reports.
What is a neural network?
A neural network is a computational model inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. It consists of interconnected nodes, or artificial neurons, that process information and make decisions based on the input data. Neural networks are a fundamental component of deep learning algorithms.
What is cross-validation?
Cross-validation is a technique used to assess the performance of a machine learning algorithm on unseen data. The idea is to split the available data into a training set and a validation set, train the algorithm on the training set, and evaluate its performance on the validation set.

